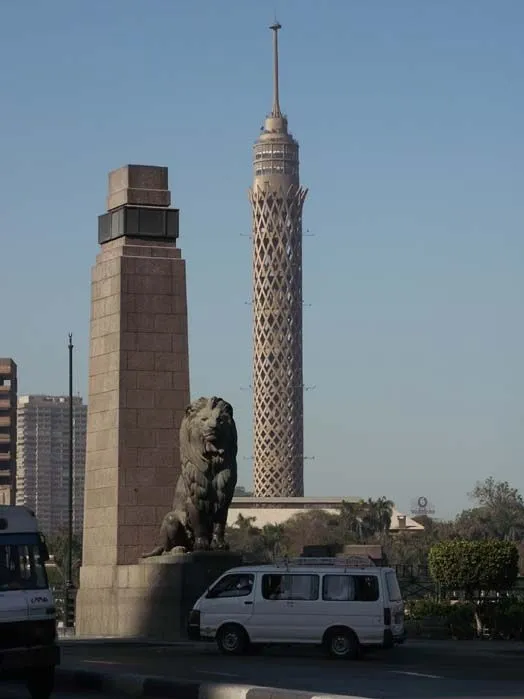
Modern Egypt
Egypt, officially the Arab Republic of Egypt (Jumhūrīyat Misr al-Arabīyah in Arabic), country in northeastern Africa and southwestern Asia. Most of the country lies in Africa, but the easternmost portion of Egypt, the Sinai Peninsula, is considered part of Asia; it forms the only land bridge between the two continents.
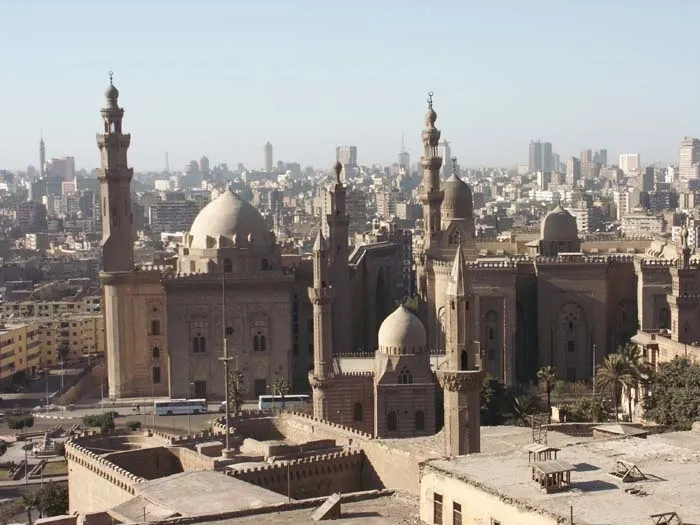
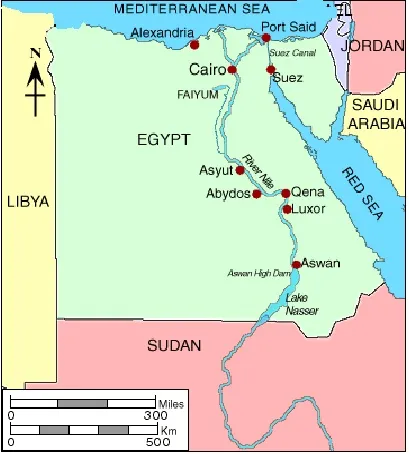
Most of Egypt’s terrain is desert, divided into two unequal parts by the Nile River. The valley and delta of the Nile are the main centers of habitation. The capital and largest city is Cairo. Egyptian Pyramids Located on the west bank of the Nile River on the outskirts of Cairo, the pyramids at Giza, Egypt, rank as some of the best-known monuments in the world. The ancient Egyptians constructed the pyramids to serve as royal tombs. Built without the use of cranes, pulleys, or lifting tackle, the massive structures stand as testaments to the engineering skills of their makers.
Egypt has been a coherent political entity with a recorded history since about 3100 bc. One of the first civilizations to develop irrigated agriculture, literacy, urban life, and large-scale political structures arose in the Nile Valley. The annual flood of the Nile provided for a stable agricultural society. Egypt’s strategic location between Asia and Africa and on the route between the Mediterranean basin and India and China made it an important hub of international trade.
Beginning in the 4th century bc, a series of conquerors brought new religions and languages to the land. However, Egypt’s rich agricultural resources, pivotal commercial position, and long-term political unity have sustained a high level of cultural continuity. Although present-day Egypt is an overwhelmingly Arabic-speaking and Islamic country, it retains important aspects of its past Christian, Greco-Roman, and ancient indigenous heritage.
Muslim Arab conquered Egypt in ad 641, and Egypt has been a part of the Muslim and Arab worlds ever since. The foundations of the modern state were established by Muhammad Ali, who served as viceroy of Egypt from 1805 to 1849, while the country was a province of the Ottoman Empire.
Britain occupied Egypt in 1882. After 40 years of direct British colonial rule, Egypt became an independent monarchy in 1922. However, British policies enforced by a continuing military occupation limited its independence. In 1952 a group of military officers led by Gamal Abdel Nasser overthrew the monarchy and established Egypt as a republic. Nasser negotiated the evacuation of the last British troops from Egypt by 1956. Egypt remains an important political and cultural center for the entire Arab world.


Back to the main topics page!






